Parliaments & Representatives
Main navigation
SPOKANE, Wash. – International lawmakers met on March 13 to discuss ways of increasing women’s political participation as disparities in representation between men and women continue on local, national and international levels.
The 68th Session of the Commission on the Status of Women, which included US, Canadian, Colombian and British leaders, focused on broad strategies to increase women’s civic representation.
“[Experts] highlighted how longstanding barriers to women’s political participation and leadership—including lack of access to political networks and resources as well as gender-based violence both online and offline—continue to undermine their inclusion and advancement in democratic processes,” the US Department of Justice (DOJ) said.
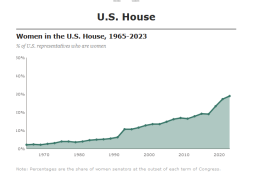
According to Pew Research Center data from March 2023, less than a third of United Nations member states have ever had a woman leader.
Click here to read the full article published by Fox 28 on 16 March 2024.
Image source: FOX 28
Thailand was once regarded as one of the most progressive in fostering gender equality. It was the second country in Asia to grant women the right to vote, as far back as 1932. A recent report, “Freedom in the World 2024”, however, shows that women in Thailand remain overlooked in politics and government at all levels.
The study by Freedom House, a US-based political advocacy organisation, said that women’s interests are generally not prioritised in political life.
The Kingdom got two out of four points in the report’s “political rights and electoral opportunities for various segments of the population” section.
“If we [women] do not work outstandingly either while working in a [House] committee or debating in parliament, we won’t be interested. It seems like we need to try harder than the men,” says Sasinan Thamnithinan, a Move Forward Party MP, in an interview with The Nation.
"Women are not decorative flowers in politics," says Sasinan, 34. “We are capable of talking about serious social issues in parliamentary debates like the men do, such as police and army reform, not just so-called feminine topics like household violence,” she says.
The lawmaker is among 32 female politicians, out of the total of 151, who secured their MP seats under the Move Forward banner in the May 14 general election. Move Forward has the highest number of women MPs among all parties.
Click here to read the full article published by The Nation Thailand on 16 March 2024.
Image source: The Nation Thailand
TOKYO -- A study group headed by Mari Miura, a professor at Sophia University's Faculty of Law in Tokyo, with an objective to achieve gender equality in Japan from local levels, has compiled a Japanese gender gap index by prefecture. Using the same method as the global gender gap index, the group collects data on women's participation in local politics, economy, education and administration. Based on the latest data for the year 2023, the Mainichi Shimbun looked into factors contributing to gender inequality across Japan and efforts to tackle the issue.
Tomoko Kogoshi, 60, served as a Yamanashi Prefectural Assembly member for four terms spanning 16 years and retired in spring 2023. For the latter half of her time in the prefectural assembly, she was the only female member.
Click here to read the full article published by The Mainichi on 19 February 2024.
Image source: The Mainichi
The Ministry of Women in Solomon Islands is looking at new legislation which could guarantee extra seats for women in provincial assemblies.
The SIBC reports in the 45 years of independent governance, 16 women have been voted into Provincial Assemblies and six into Parliament.
Endorsed in December by the now caretaker government, the proposed amendment would establish temporary special measures (TSM) to guarantee additional seats for women in Provincial Assemblies.
The TSM endorsement by Cabinet was the result of approximately six years of work led by several ministries and partner organisations including; Women's Rights Action Movement (WRAM), Solomon Islands National Council of Women (SINCW) and the Honiara City Council (HCC), the SIBC reported.
Click here to read the full article published by RNZ on 13 February 2024.
Image source: RNZ
With the Women’s Reservation Bill being passed in Parliament last year, the debate on whether quota within political parties or in Parliament and State Assemblies may be the best route for increasing women’s representation in politics seems to have come to an end. The Assembly elections in Rajasthan showed that the only way for increasing women’s political participation seems to be to provide them reservation in Parliament and State Assemblies. In the elections, the women candidates of both the Congress and the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) put up dismal performances.
Click here to read the full article published by The Hindu on 12 February 2024.
Image source: The Hindu
CRRC Georgia surveyed the Georgian public on attitudes towards gender equality in politics and obstacles faced by women in politics in Georgia.
Gender equality in politics is an important issue globally, and Georgian policy on the issue has been developing in recent years. Georgia introduced mandatory gender quotas for proportional party lists in 2020, extending this provision until 2032. The legislation stipulates that at least one out of four candidates submitted to the Central Election Commission, and provides financial support to parties that nominate more women.
Despite these policy changes, much remains to be done to ensure gender equality in practice. In the 2020 parliamentary elections, only three political parties and one electoral bloc benefited from the financial incentive mechanism for nominating more female candidates than the mandatory gender quotas required. A study on mandatory gender quotas in Georgia found that in 2022, women still made up only 19% of Georgia’s parliament.
Click here to read the full article published by the OC Media on 6 February 2024.
Image source: OC Media